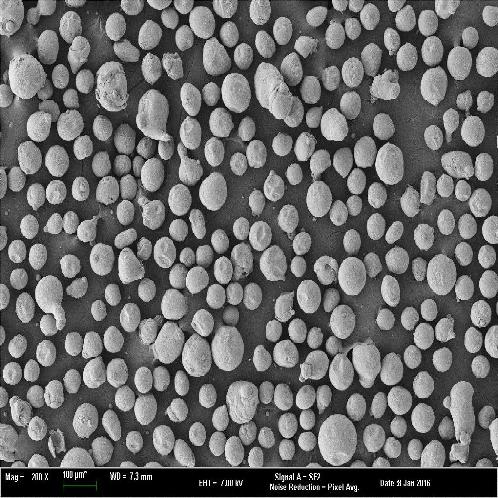
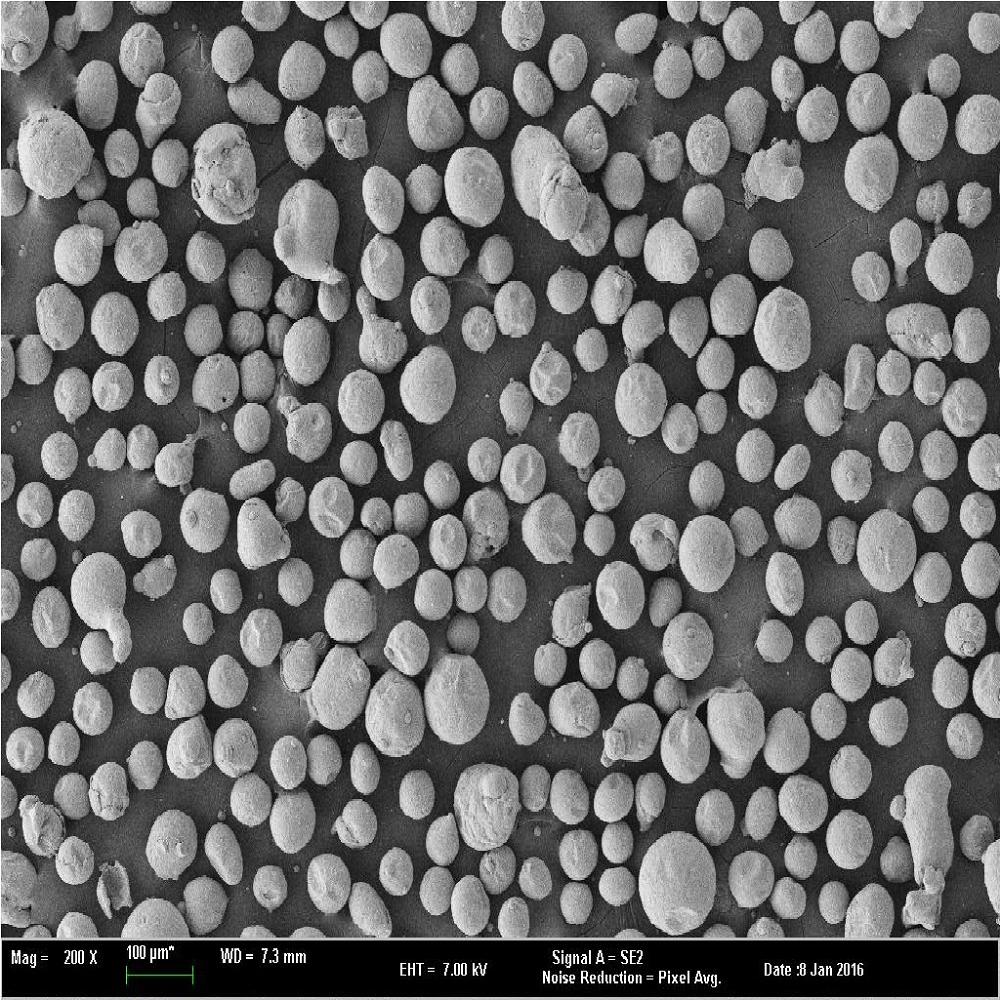
Magnesium Powder
-
Payment
OT , T/T , WK
-
MOQ
Negotiable
-
Supply Details
Customization Sample Order
Contact us because it will vary depending on the order quantity.
-
Country of sale
Asia, Americas, Europe, Middle East, World Wide
-
PRICE
-
FOB
Depend on quantity
-
ITEM SPECIFICS
-
Brand
Model Magnesium PowderHanaAMT
-
origin
Republic of Korea
-
Size(Capacity)
30~50 mesh (300~600 um), 50~100 mesh (150~300 um), 100~200 mesh (75~150 um), 200~325 mesh (45~75 um)
-
Material
Magnesium
-
Color
Silver
-
Features
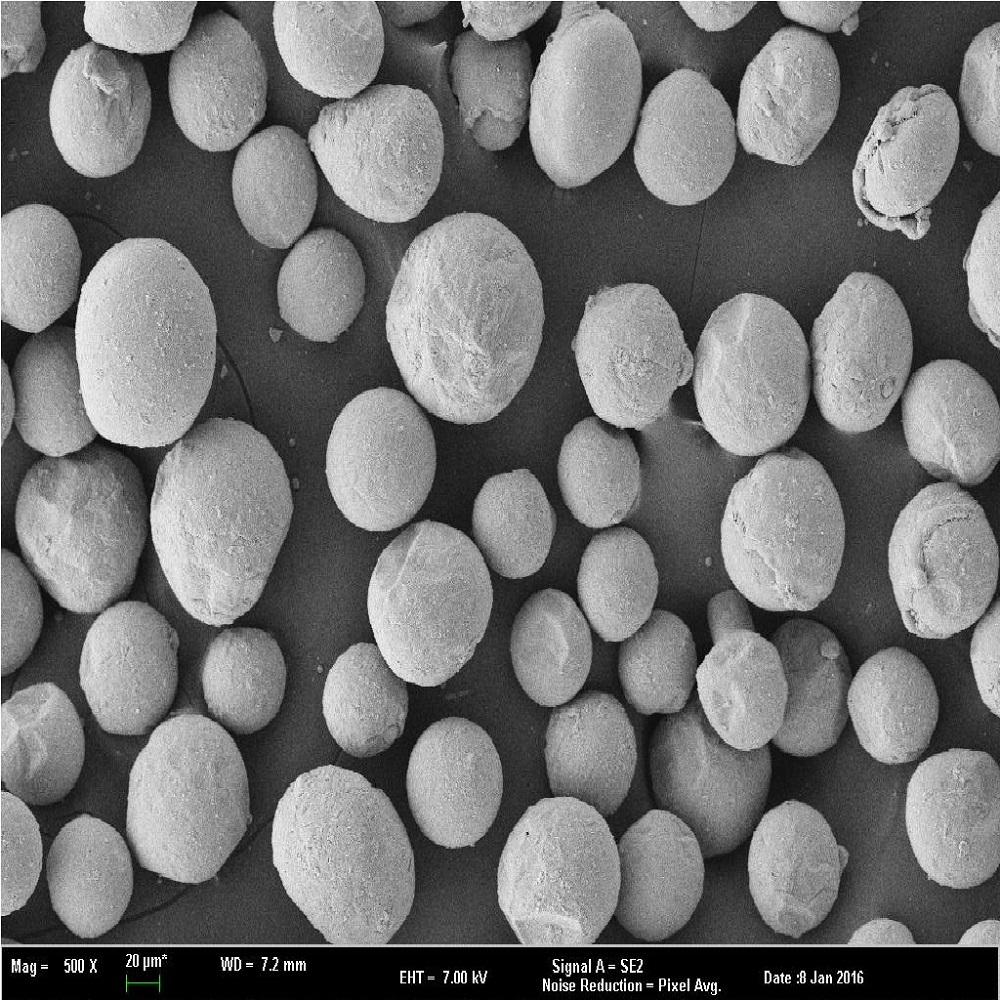
Spherical powder is produced which is then screened and blended to customer specifications.
-
Condition
Spherical / Chip or Flake
PRODUCT DESCRIPTION
[Features]
Gas Atomization Process
Gas Atomization (Gas Atomization Process) is one of the most common methods for manufacturing metal powders, which is a process for manufacturing fine powders by ejecting gas into molten metal. During the gas automization process, metal powders are obtained when the high pressure gas jets from the nozzle gives the strong impact energy to molten metal droplets during their fall through the orifice. The changes of the factors such as gas type and pressure, internal diameter of orifice and nozzle type have an effect on the major characteristics such as powder properties, shapes and particle size distribution.
⦁ Properties of HANA AMT’s metal powders that manufactured by gas atomization
- Globular powders with homogeneous particle size distribution
- Easy to be synthesized and mixed with other element powders
- Excellent liquidity of powders
- High density of powders
- Efficient control of powder oxygen density
- Possible to manufacture powders with irregular shapes
The magnesium metal-powder which is produced in HANAamt reveals the following unique characteristics.
⦁ Spherical powder is produced which is then screened and blended to customer specifications.
⦁ Atomized powder exhibits excellent Fluidity and is easy to mix with other materials and still retain good flow characteristics and low viscosities.
⦁ It exhibits higher packing density.
⦁ It has superior stability.
USE Fine and atomized powders are widely used by the military industry in a range of flare and ordnance applications, notably decoy flares and illumination flares. Decoy flares made from magnesium burn white hot and the intense heat of the pyrotechnic candle consumes the flare housing. Such flares are designed to defeat a missile's infrared tracking capability, thus making the use of magnesium instrumental in the protection of military helicopters and aircraft. Ground illumination flares are designed to descend by parachute and illuminate ground terrain and targets.
[Specifications]
Magensium
PAYMENTS DETAILS
This supplier supports payments for offline orders
- WK
- OT
- Telegraphic Transfer : T/T
- Name : Chang Bean Im
SHIPPING
Shipping from :
Republic of Korea
- 75 Gangni 1-gil Ochang-eup Cheongwon-gu (28126)
- Air Cargo : Please contact us for inquiry on carriers
- Sea Freight : Please contact us for carriers inquiry
- Sea Freight : impossible
- Please contact your administrator for detailed information.
- Name : Ch***,Im***
- Tel : 82-43-211-0046
HANAAMT CO., LTD.
The person in charge
HONG MOULE KIMAddress
75 Gangni 1-gil Ochang-eup Cheongwon-gu, Cheongju-si, Chungcheongbuk-do (28126)
Introduction
To make the neighborhood happy through the materials and parts industry, a company called HanaAMT was established. We are developing customer-centric products through innovative ideas. Through continuous research and development, we will continue to grow and evolve into a company with the world's best technology and customer satisfaction. We are in the business of manufacturing and selling metal powder and manufacturing glass.
You can find more detailed products through the website (www.hanaamt.com).
-
- Business Type :
- Manufacturer
-
- Main Product :
- s
-
- Established :
- 2010-01-01
-
- Total Annual Revenue :
- 4~5 billion (KRW)
-
- Total Employees :
- 11~50 people
Please suggest a variety of your ideas such as design, impact, enhancements, etc
Captcha Required
Please enter the text on the left image to prevent automatic input.
0 / 4000
질문이 없습니다.
CUSTOMER REVIEWS (0)
TRADE EXPERIENCE
-
- Total revenue
- 4~5 billion (KRW)
-
- Total export revenue (previous year in USD)
- 1
-
- Number of foreign trade employees
- 11~50 people
COMPARISON TO SIMILAR ITEMS more
- No Items
- supplier level
-
 PLATINUM
PLATINUM
- HANAAMT CO., LTD. Seller's Store
- Seller's Store url
- Response Level
★ ★ ★ ★ ★

- Supplier Level
★ ★ ★ ★ ★

- Transaction Level
★ ★ ★ ★ ★